Module description¶
EAGER comes with lots of different modules for different use cases, thus enabling the user to configure the pipeline in a fine granular way. This section describes the different modules in more detail than e.g. the user tutorials that are offered here in the documentation too.
FastQC¶
This module can not be configured and is utilized to gain first insight into a raw sequencing dataset to determine important basic statistics, such as for example GC content and average read lengths prior to modifying the data. This should be used whenever you want to analyze data coming from sequencing without having an idea if even sequencing was successful as it creates basic plots showing whether the data is suitable for further downstream analysis.
Adapter RM / Merging¶
Enables you to select either our in-house adapter clipping and read merging application Clip&Merge or AdapterRemoval v2.2+ for adapter removal and read merging.
Clicking on the Advanced button next to this, you will get either the advanced configuration for Clip&Merge as depicted below:
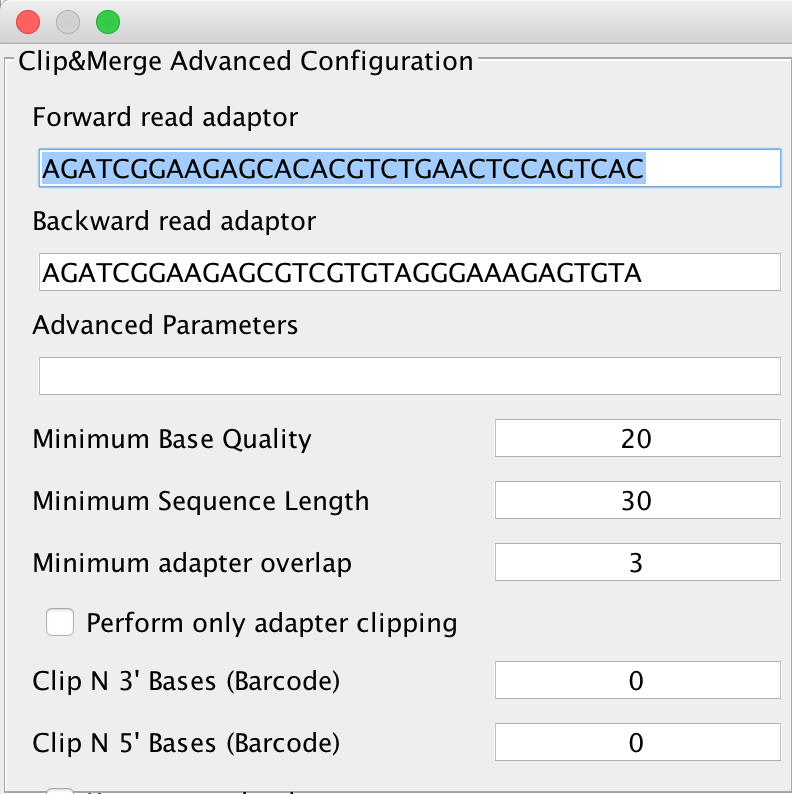
You can select forward and reverse read adapters here that are then subsequently clipped off your sequencing reads during analysis. Furthermore, Clip&Merge performs a base quality trimming of unmerged reads, filters out sequences falling below a certain length. Also, you can specify the minimum adapter overlap length you require (the number of bases of your specified adapter sequence required to overlap with your sequencing read). If you don’t want to merge your reads, you can also specify to only clip adapters without merging reads afterwards. Barcodes are supported too, you can specify to trim bases from both 3’ and 5’ ends as well in the application. Another feature is available to only include merged reads into downstream analysis. Unmerged reads are kept in separate files, one for forward and one for reverse reads, stored in the same folder than the merged ones but unused for further downstream analysis.
Warning
Specifying wrong adapters, trimming too many bases here will result in poor analysis performance, so make sure beforehand which adapters to use in your analysis. For single ended data, it is advisable to use AdapterRemoval v2, as it is more sensitive to very small adapter fragments.
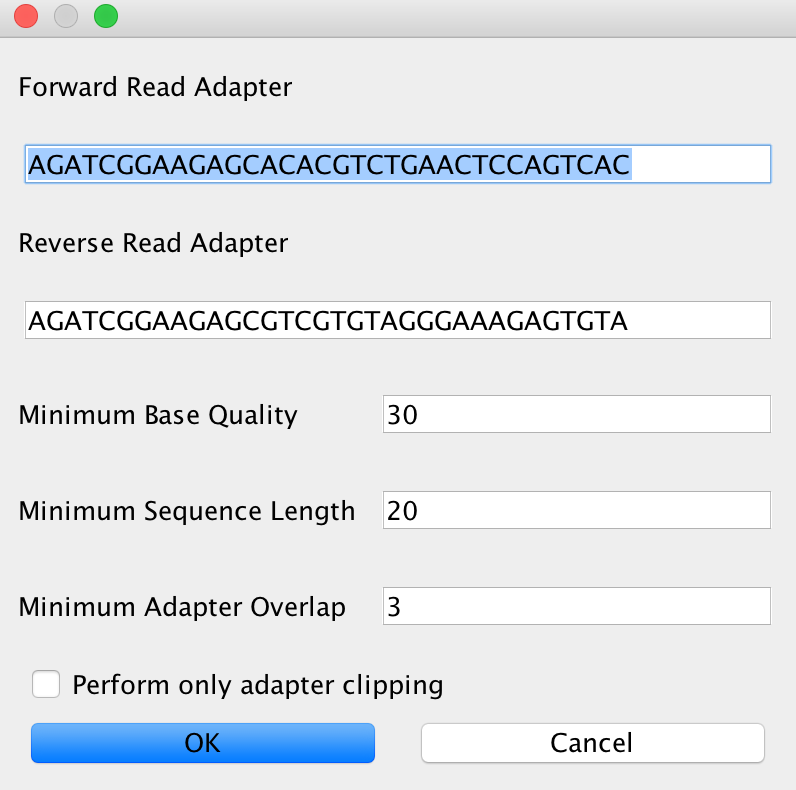
In case you selected AdapterRemoval, you will be able to select basically the same criteria than for Clip&Merge. The Advanced setting will look like this in that case:
Note
It is completely up to you which adapter removal and merging procedure you’d like to use in your analysis. Recommendation: Use Clip&Merge for paired-end data with subsequent merging and AdapterRemoval for single-end data and paired-end data without read merging.
QualityFiltering¶
For downward compatibility reasons, we have the possibility to filter sequences based on quality in the pipeline, too. This tool has been replaced by Clip and Merge and is therefore deactivated by default when Clip and Merge is selected.
Mapping¶
These modules configure the read mapping process. EAGER currently features four mapping algorithms, which can be used. BWA, CircularMapper and BWAMem have been tested intensively, Bowtie2 works well too, but can not be configured in detail as of now. Stampy is currently to be seen as experimental and may not work in all conditions.
BWA¶
This is the default mapping algorithm, largely used for mapping reads to ancient genomes and has been used in many ancient sequencing projects. If you’re not sure what to use, use this algorithm.
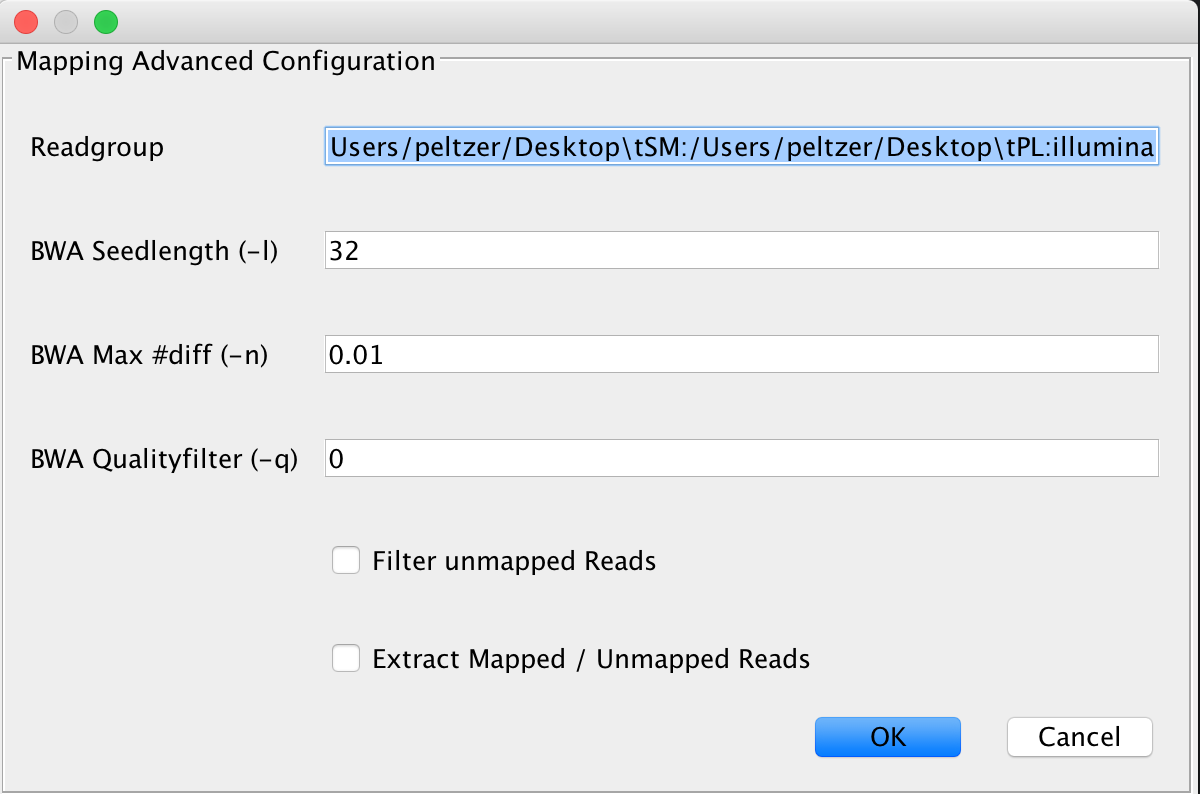
Note
If you’re not sure which parameter you should be using for -n, use this web service to determine an optimal parameter for your data using an interactive choice tool
Note
In many ancient DNA sequencing projects, analysts turn off the seeding factor -l by setting it to a value significantly larger than the read length is done to gain better mapping rates for damaged ancient fragments. In case you receive bad mapping results, consider disabling seeding.
CircularMapper¶
This relies on the BWA mapper, but utilizes some tricks to obtain better mapping results on circular genomes. You can set the elongation factor to longer values in case you have data that includes longer reads. The Reference to extend value needs to describe the FastA entry that is used by the mapper for extension, e.g. if you have multiple chromosomes in your FastA reference, you need to specify one (or more, separated by a ;) chromosome to be extended by the algorithm.
Note
Make sure that you use the first part of your reference identifier, for example until the first space is reached as identifier. Something like gi|123445| works, whether our matching method doesn’t work with gi|34425| 12345. Don’t worry about the identifier containing pipe symbols, this is taken care of.
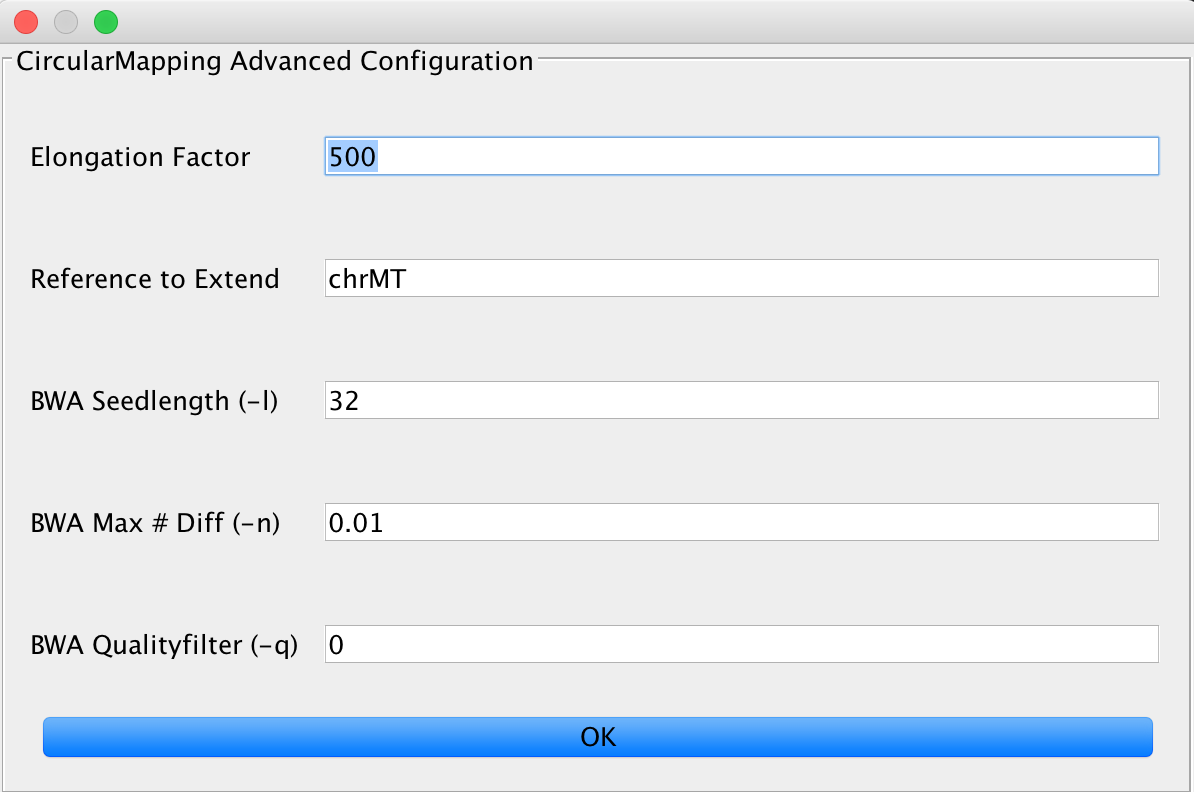
You can further adjust the BWA mapping parameters here, too.
BWAMem¶
BWAMem can not be configured in the pipeline and is executed with default values if you select this algorithm. We will add more parameters in an upcoming version of EAGER.
Bowtie2¶
You can specify parameters for Bowtie 2 here. These will be simply passed through to the mapping algorithm.
Warning
If you specify parameters that are either non-existent or incorrect for the mapper, your analysis will fail subsequently.
Stampy¶
Stampy can not be configured in the pipeline and is executed with default values if you select this algorithm. We will add more parameters in an upcoming version of EAGER.
Complexity Estimation¶
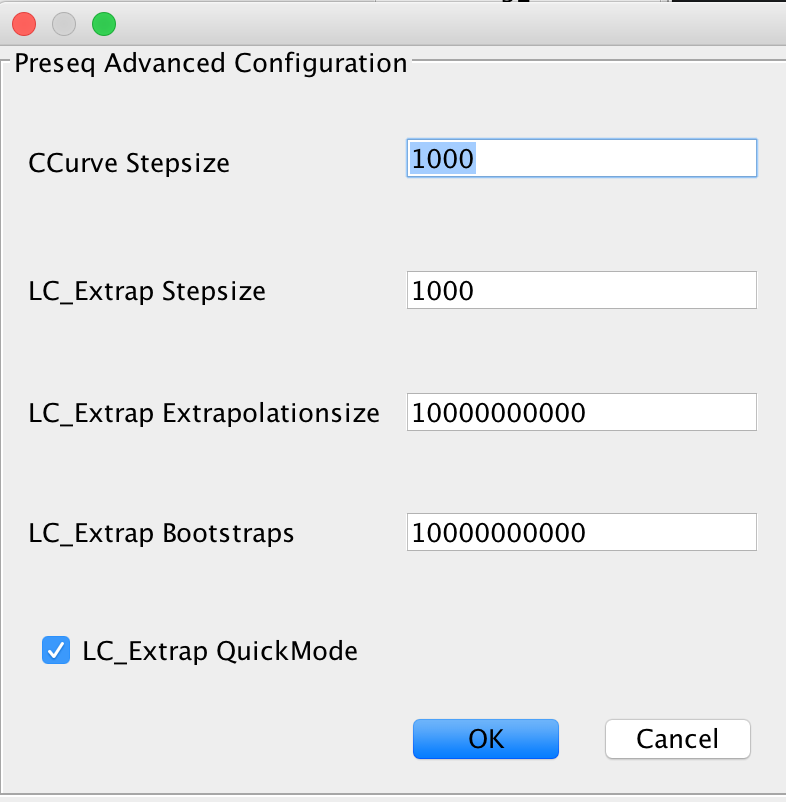
The complexity estimation is done using Preseq, running both components c_curve and lc_extrap after each other to determine the library complexity. Enable this module if you are testing a new sequencing library for complexity, to determine whether further deeper sequencing is justifiable.
Remove Duplicates¶
EAGER provides two different duplicate removal procedures: The DeDup and the MarkDuplicates method (provided by Picard).
DeDup¶
Use this if you’re working with merged reads, single ended reads or a mixture of merged and remaining single ended reads that could not have been merged previously. This produces increased coverages as merged reads are treated correctly by looking at both ends of the merged reads instead of only considering start positions of these reads.
MarkDuplicates¶
Use this if you’re working with paired end data, that has not been merged.
Contamination Estimation¶
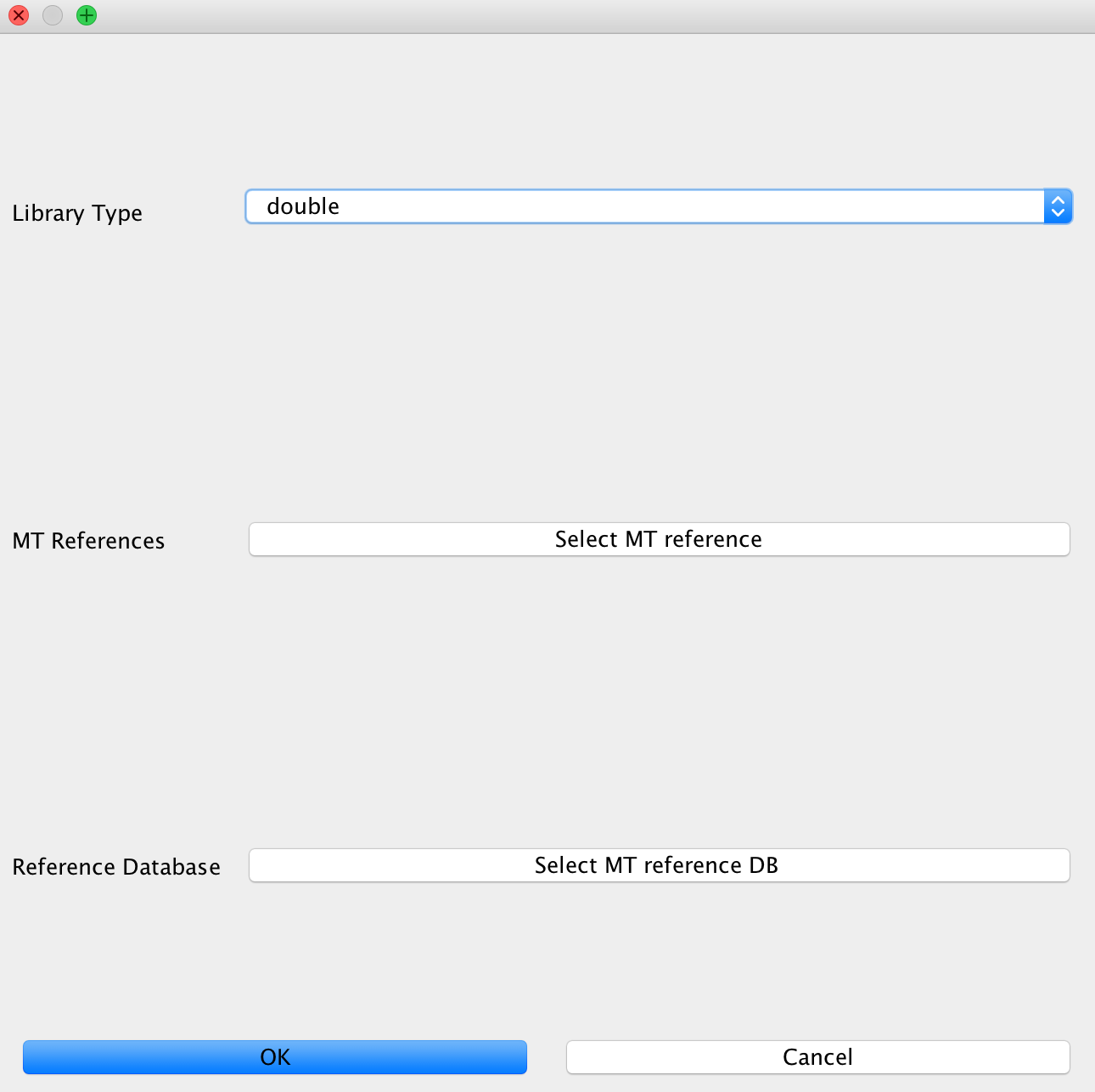
This module is used to configure contamination estimation using schmutzi. In order to make this work, you will need to specify whether you have single stranded or double stranded libraries sequenced. Afterwards, you will need to specify the mitochondrial genome you would like to test against (usually of your human genome). Finally, select the folder with frequency data of putative mitochondrial sequences.
Note
If you are not working on mitochondrial data and did not select this, you may only specify the library type without configuring the other options. You don’t need to specify these for bacterial data, too as the mitochondrial test can only be performed with a library of putative mitochondrial reference genomes.
Coverage/Statistics Calculation¶
This module handles coverage and other statistics calculation using QualiMap. This is enabled by default and can not be turned off at all.
MapDamage Calculation¶
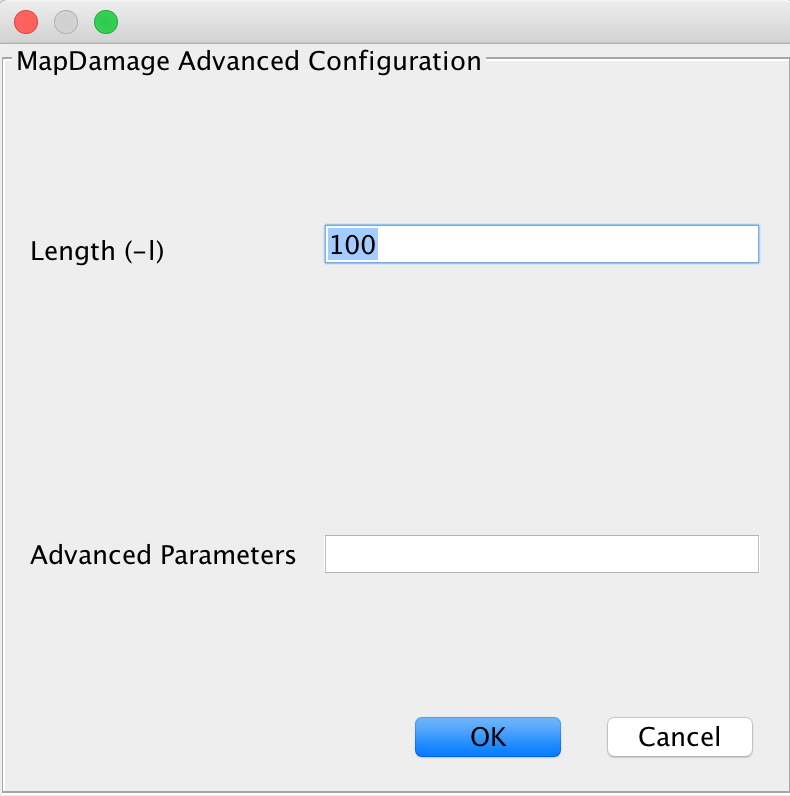
This module handles calculation of DNA damage, which is used for authentication of samples. You will get a plot and damage statistics telling you whether you truly see ancient fragments in your dataset or not. You may specify more advanced parameters here, too.
SNP Calling¶
This section is used to specify methods for genotyping your mapped datasets. Note that these depend on your mapping results, meaning that samples containing very few reads will not result in good genotyping results either.
UnifiedGenotyper¶
You can set parameters for genotyping using the UnifiedGenotyper here. In case you have a reference database of known variants in VCF format for your respective organism (e.g. dbSNP for humans), you may specify this here, too. Refer to the GATK documentation to receive up to date information about the parameters offered here in EAGER.
HaplotypeCaller¶
You can set parameters for genotyping using the HaplotypeCaller here. In case you have a reference database of known variants in VCF format for your respective organism (e.g. dbSNP for humans), you may specify this here, too. Refer to the GATK documentation to receive up to date information about the parameters offered here in EAGER.
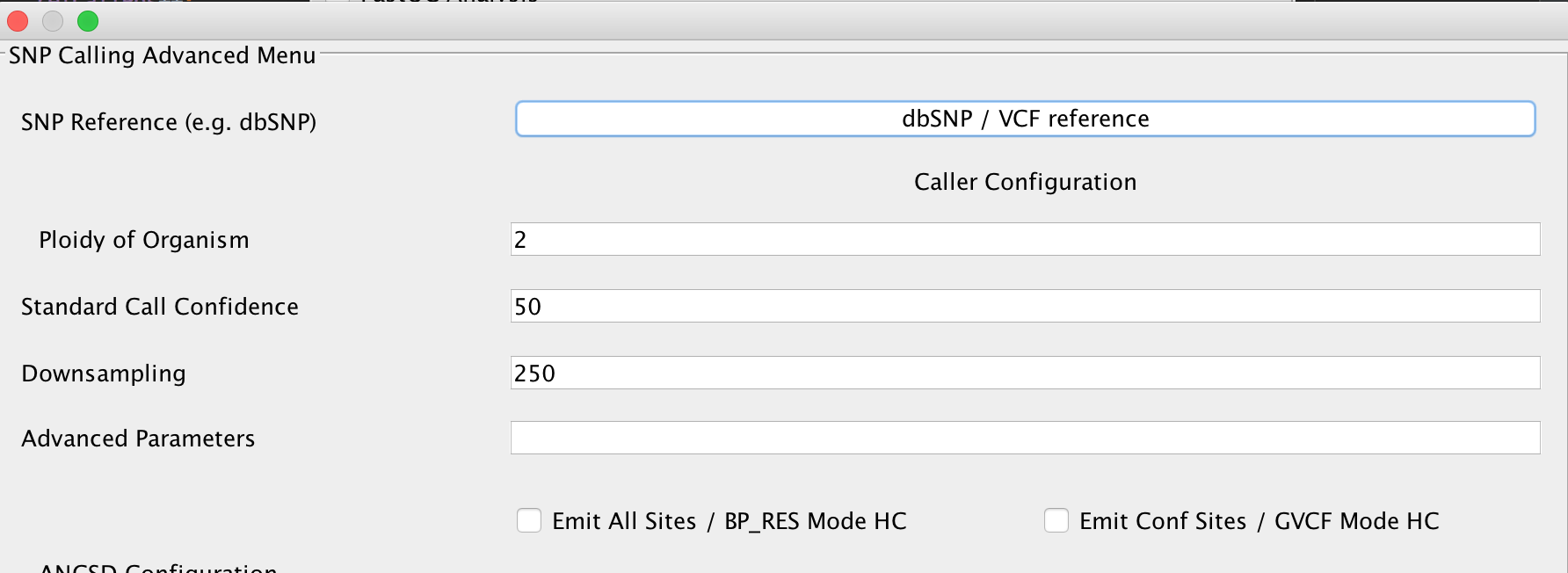
Warning
Selecting the EMIT All Sites? option should only be done on small reference genomes. For a human genome, this produces uncompressed VCF files in the size of up to 90GB/sample. For some purposes, it might still be required but in most cases its not advisable to turn this on.
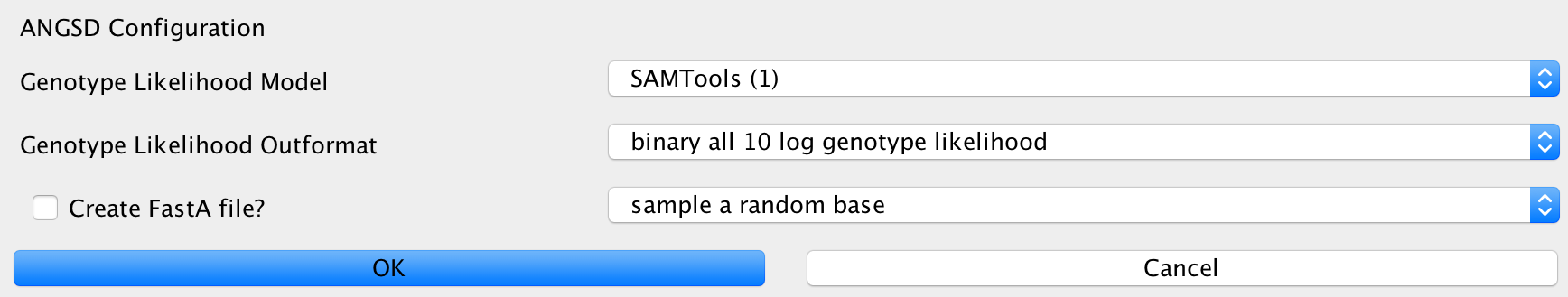
ANGSD¶
This can be used to configure the ANGSD method for genotyping low coverage genomes using genotype likelihoods. You can specify the likelihood model to use, the output format you want to generate and method to make a call at a certain position. Furthermore, you can specify whether you’d like to generate a FastA sequence of your calls in the end.
SNP Filtering¶
This can be used to filter variants based on minimum quality of a genotyping call and a minimum coverage using the GATK VariantFilter application.
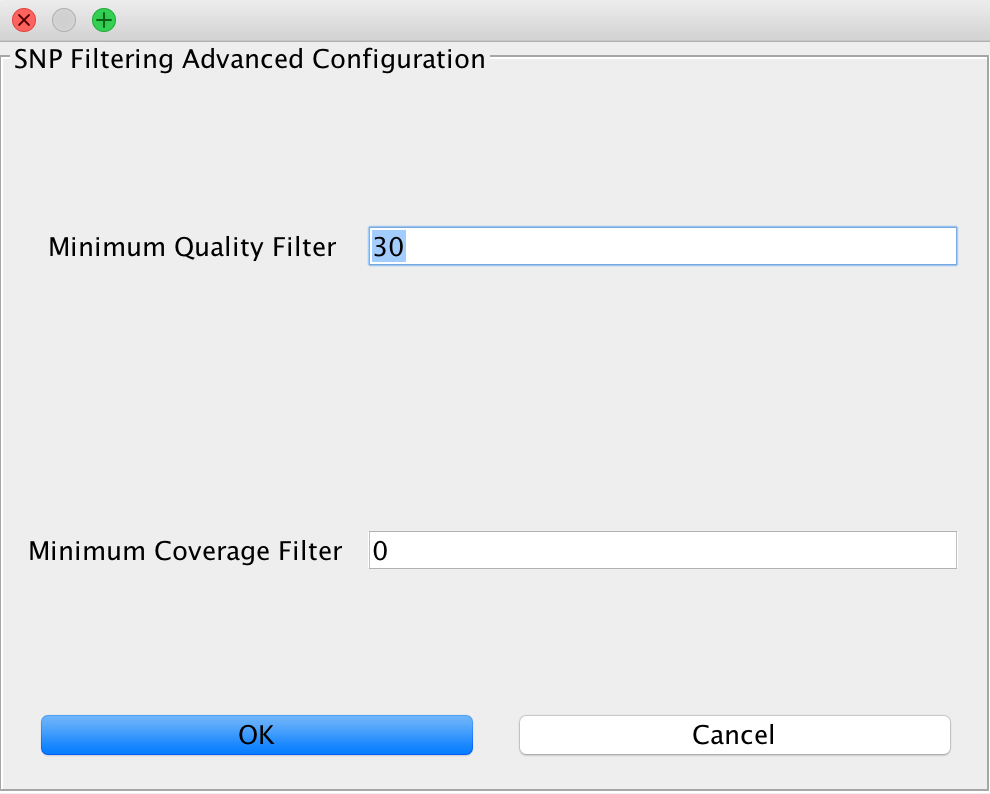
Note
Note that this only has an effect on genotypes. If you used the ANGSD method producing genotype likelihoods as an output format, you will not be able to perform SNP filtering using this method.
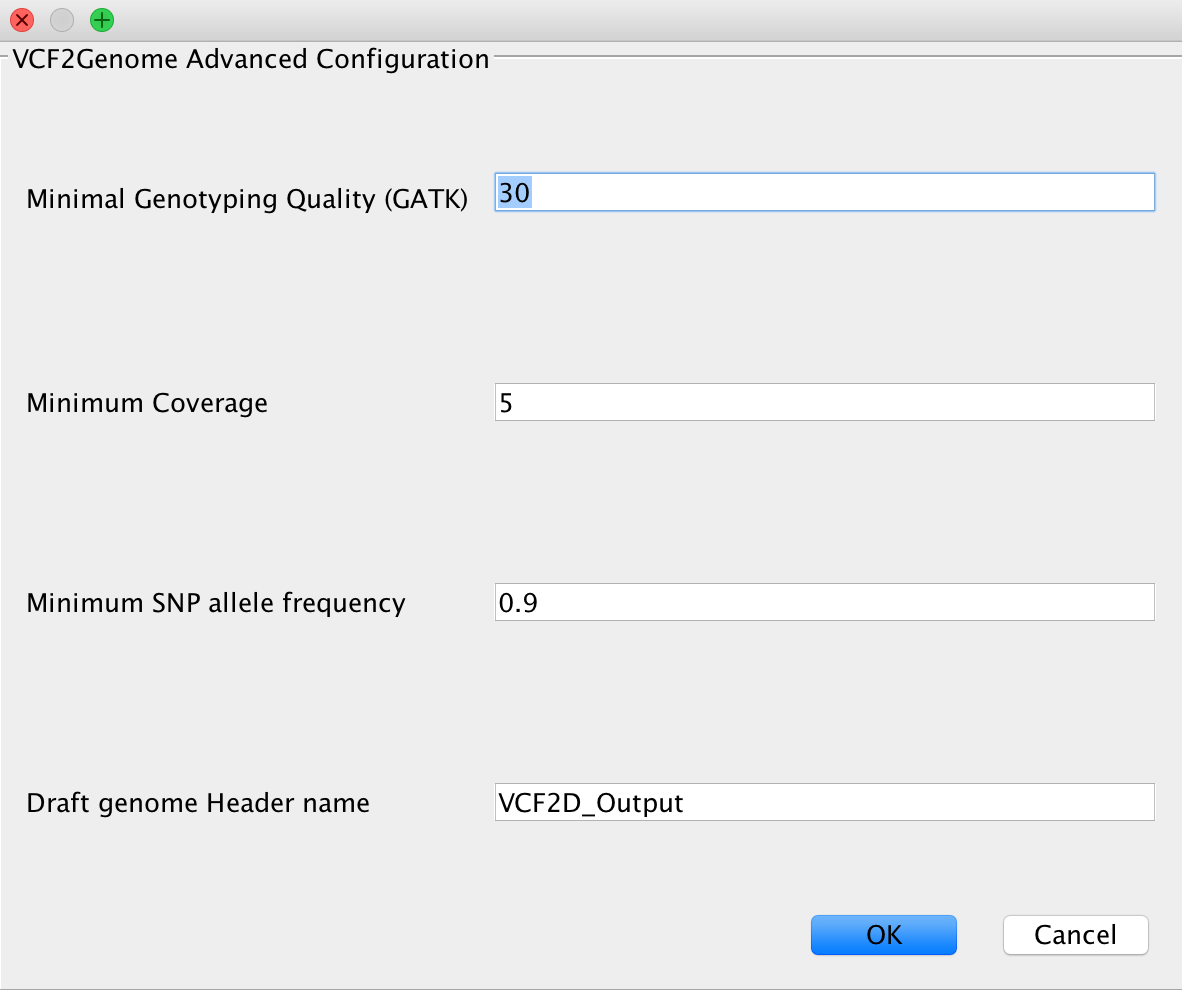
VCF2Genome¶
This method can be used to generate FastA files incorporating called variants from a generated VCF file. Particularly useful for bacterial data, it allows the user to select minimum genotyping quality, coverage and SNP allele frequency to consider a call as true. For a more detailed description, see the paper citations.
CleanUp¶
This module is responsible for cleaning up intermediate results. Mainly, these are files generated during file conversion, e.g. SAM files and unsorted BAM files that have been converted to sorted BAM format already and can thus be safely deleted.
Note
This will only delete files that are redundant, e.g. from which there exist copies with the exact same content.
Create Report¶
This will generate a report of your whole analysis run. After each sample, the CSV file gets updated by EAGER automatically. This way, you can basically evaluate your results while waiting for other samples to finish.